Functional Performance of Electropolishing
Electropolishing is a process that uses an electric current with the workpiece as the anode in an electropolishing solution. Surface peaks dissolve preferentially, yielding a smooth, high-gloss surface. No oils or abrasives are used, and no mechanical force is applied to the stainless surface.
※ Suited for clearly defined targets such as improving cleanability and smoothness of large panels, or removing micro-burrs generated by machining.
Abel’s Proprietary Electropolishing “Belclean” for Enhanced Stainless Functionality
Our electropolishing establishes a comprehensive clean-processing technology called “Belclean,” designed to meet stringent requirements for industrial equipment used in pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, food, and energy.
Key Characteristics of Electropolishing
1: Corrosion Resistance Improvement (Chromium enrichment at the surface enhances corrosion resistance)
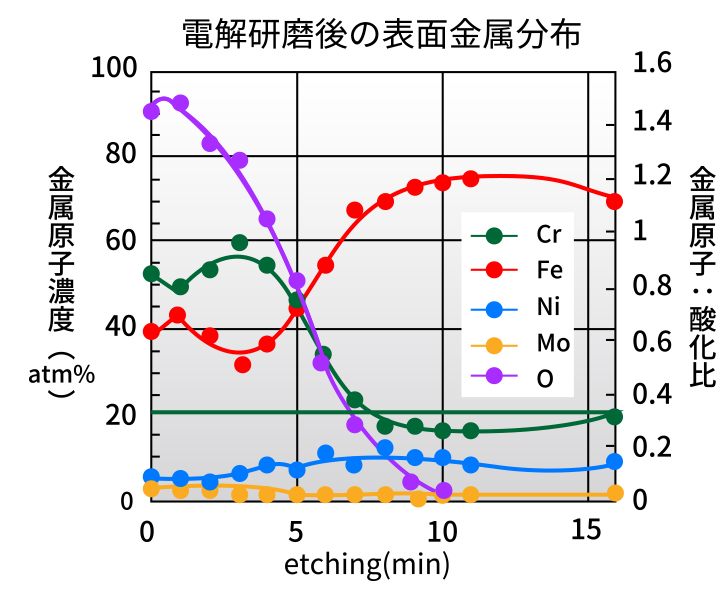
Electropolishing enriches chromium at the stainless surface, improving corrosion resistance.
As shown below, Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) indicates increased chromium concentration at the extreme surface. In a ferric chloride corrosion test (JIS G0578), mass loss decreased to one quarter, indicating roughly four times higher corrosion resistance.

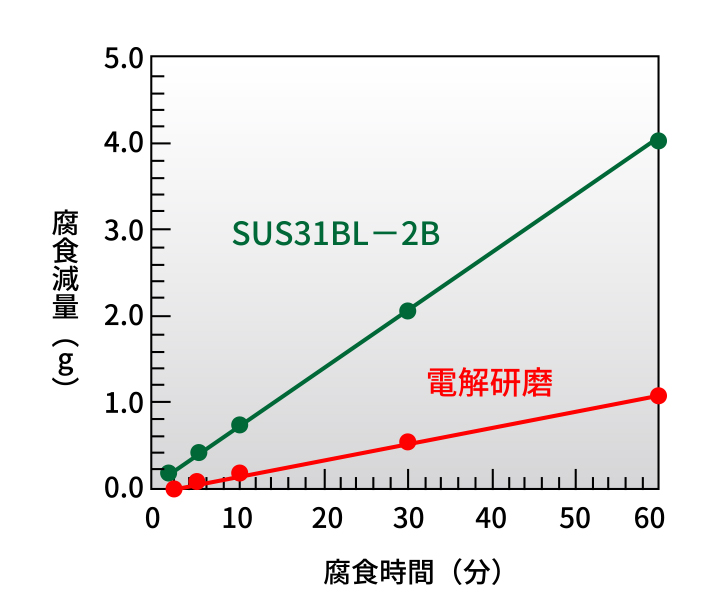
Ferric Chloride Corrosion Test
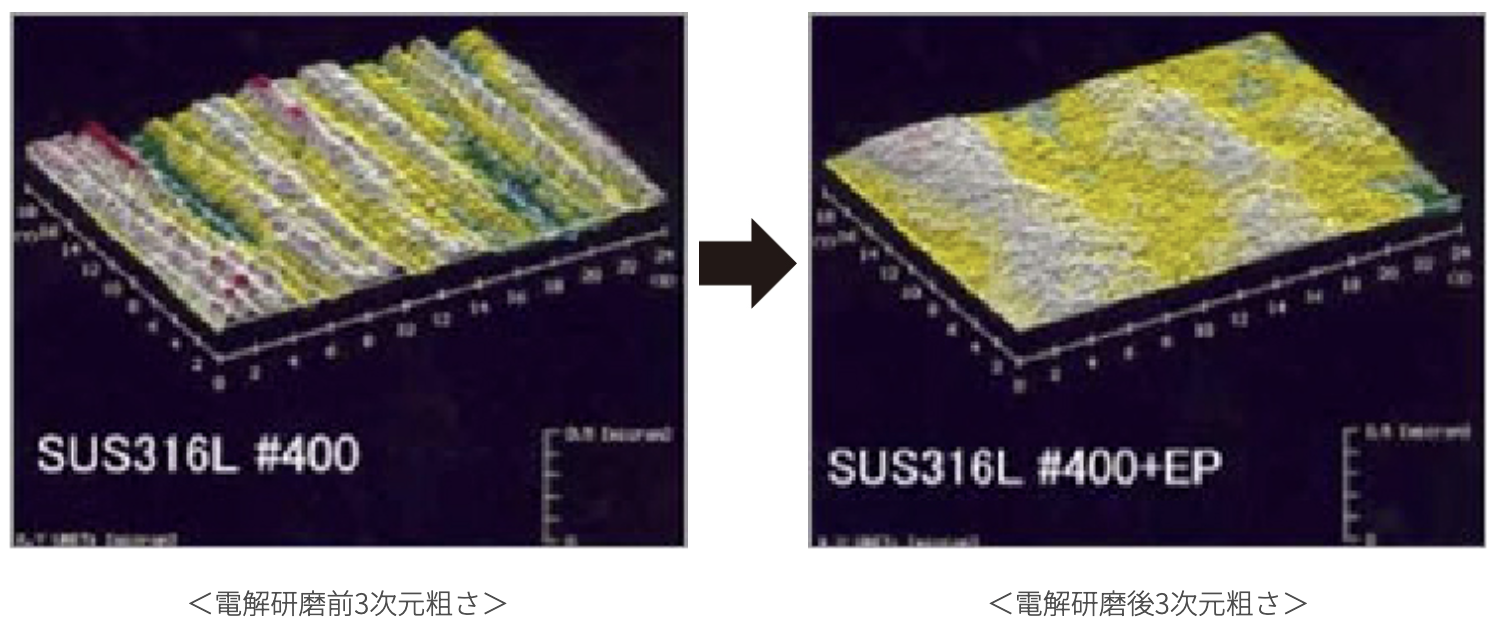
2: Smoother Surface and Higher Gloss
Removing micro-roughness produces high gloss and smoothness. When current is applied, metal dissolves as cations. At the immediate surface, these ions interact with the solution to form a highly viscous layer.
The bulk electropolishing solution has low electrical resistance and conducts well, whereas this viscous layer has high resistance. Current flows far more readily through region [A] than [B] in the right figure. As a result, peaks—where current density is higher—dissolve selectively, and the surface smooths over time.
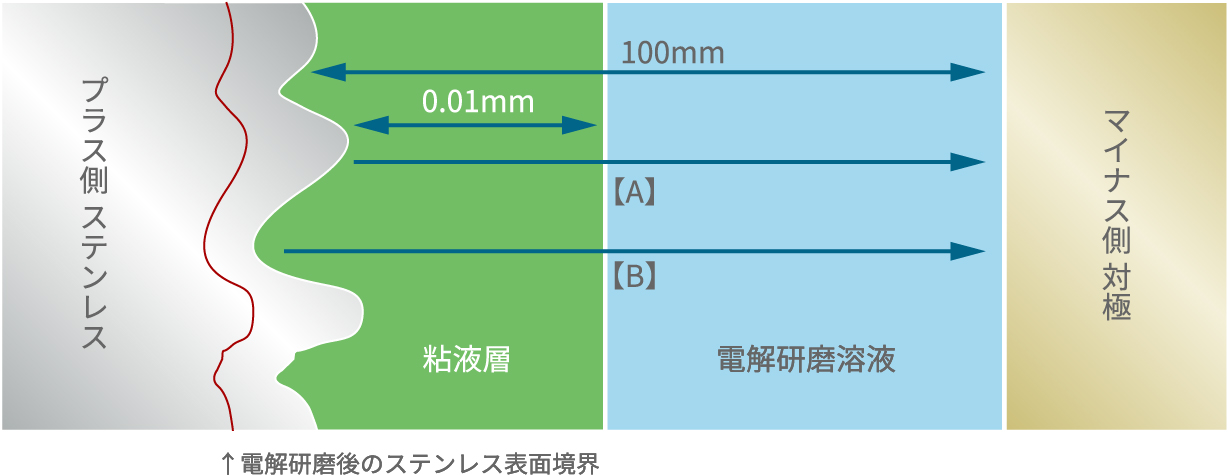
Peaks dissolve preferentially, and the surface smooths over time.
During electropolishing, gloss increases alongside smoothing.
By removing roughness smaller than 1/100 μm, random light scatter at the surface is reduced, yielding a bright reflective finish.
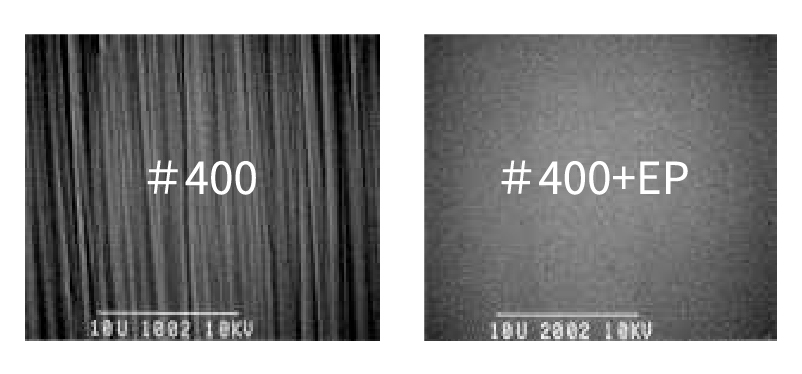
Surface micrograph
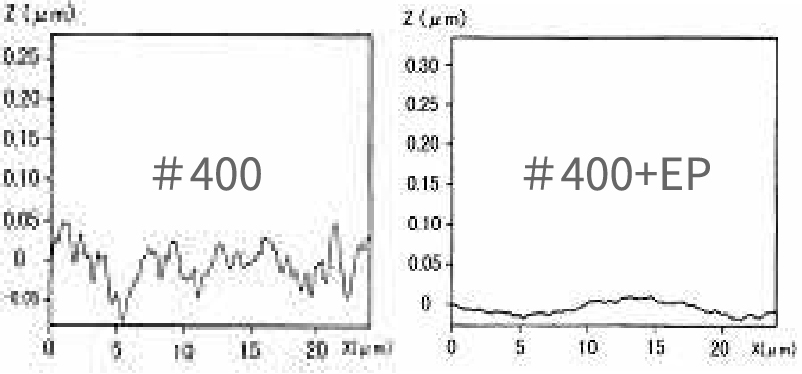
Roughness profile (enlarged)
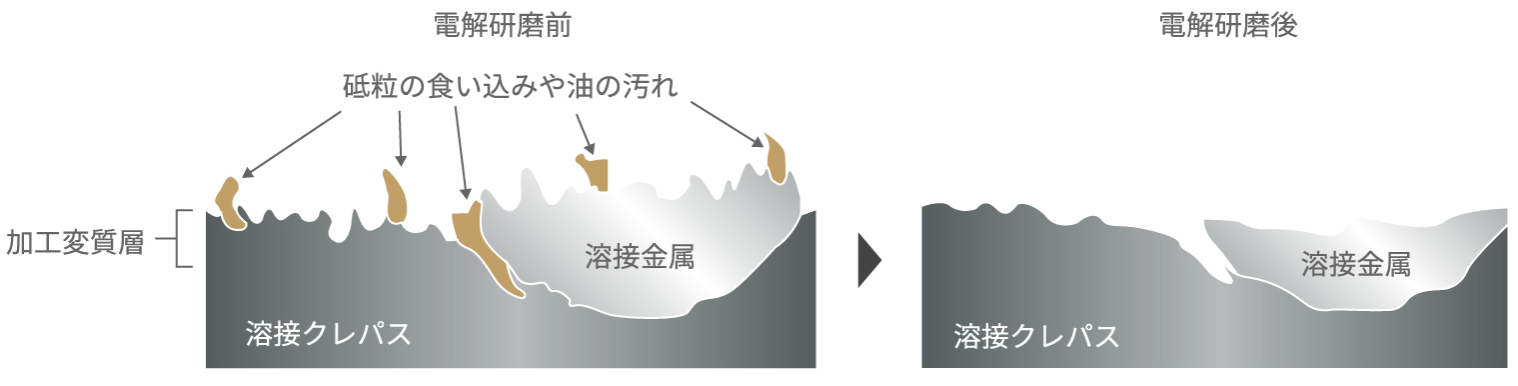
3: Cleanability
Electropolishing restores functions degraded by mechanical polishing or fabrication, delivering a clean finish. Mechanical polishing and welding leave various impurities on stainless surfaces. “Belclean” dissolves a controlled amount from the surface, removing these impurities.
This cleans the surface and recovers functionality (e.g., corrosion resistance) reduced by mechanical polishing.
Post-process verification includes wipe tests to confirm the absence of residues.
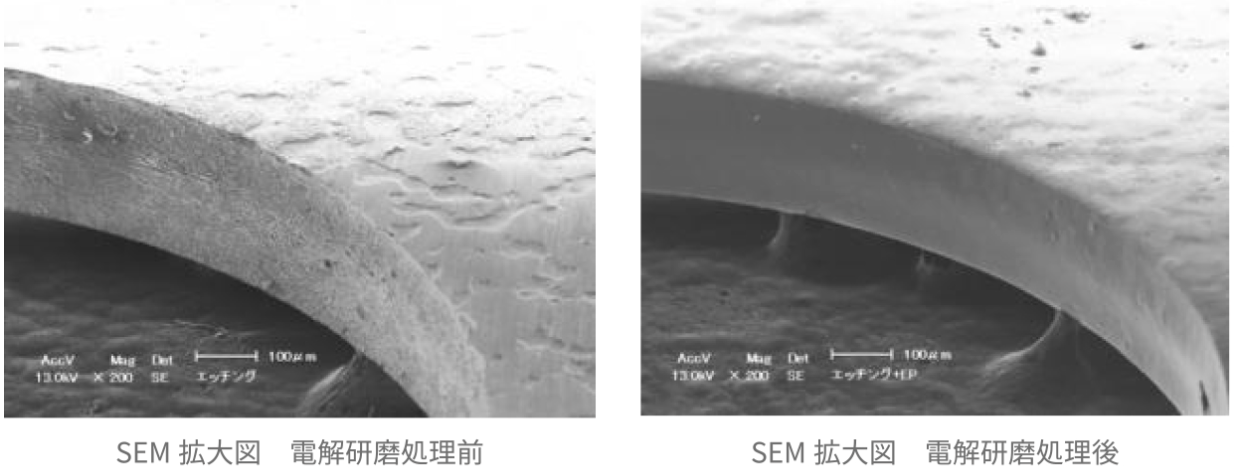
4: Decontaminability (reduces adhesion of external contaminants/impurities)
By removing contamination from mechanical polishing and smoothing the surface—including eliminating micro-roughness—decontaminability improves significantly.
Stainless surfaces are cleaned
Reduced adhesion of external contaminants
If contaminants adhere, subsequent decontamination is more effective
Significant reduction in decontamination maintenance
Track Record
As clean energy is sought, nuclear power plays a significant role.
Electropolishing is used on stainless components in nuclear facilities to improve corrosion resistance and decontaminability, reducing wall-thinning and shortening inspection outages.
Electropolishing of stainless panel materials for awning installation work at nuclear-related facilities → improved decontaminability
- Over 5 years of track record
- Delivered to three electric utilities in western Japan
- Dozens of projects including planned (as of January 2010)
- Demonstrated quality improvements versus other companies’ electropolishing
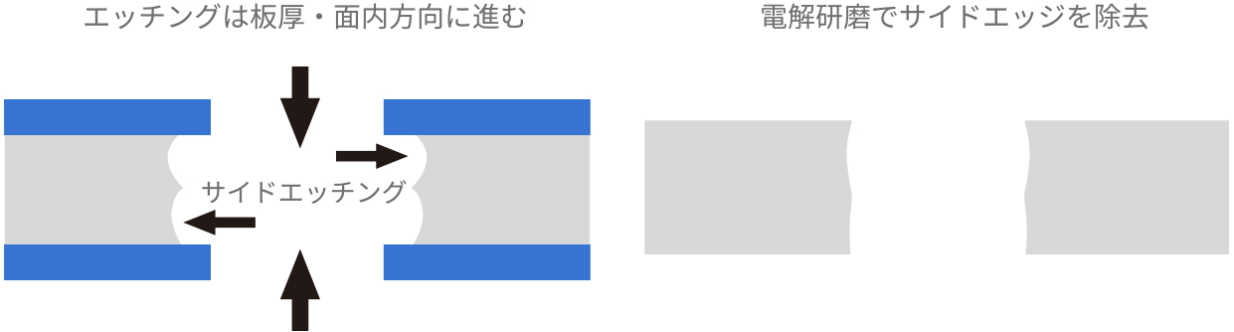
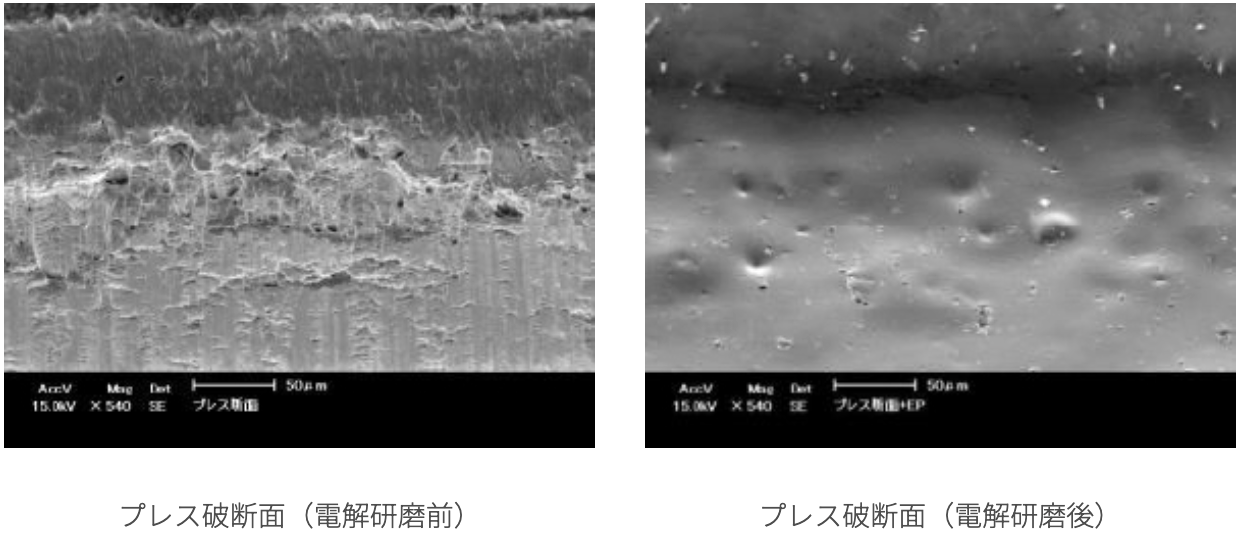
5: Removal of Micro-burrs
Capable of removing micro-burrs generated by etching or punching.
Processable Size
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Effective process size (mm) |
800H × 800L × 2000W ※ Please consult us separately for three-dimensional structures.
|